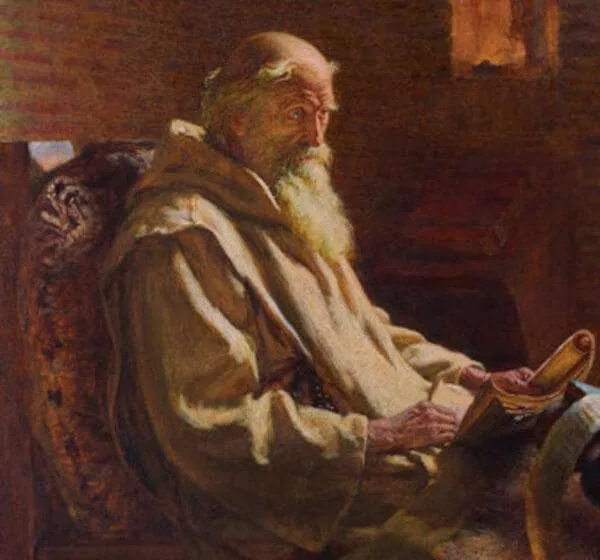
Saint Bede the Venerable, Priest and Doctor
c. 673–735; Patron Saint of lectors, scholars, English writers, and historians; Pre-Congregation canonization; Canonization confirmed and proclaimed a Doctor of the Church by Pope Leo XIII in 1899
In the fourth-century, many in Roman-controlled Britain were Catholic. However, after the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the fifth century and the removal of Roman troops from Britain to defend the homeland, Britain began to encounter threats from the Scottish and Irish. Angles and the Saxons from central Europe arrived to assist Britain but then conquered Britain themselves. By the sixth century, Britain had become known as Anglo-Saxon England and was divided into nine smaller kingdoms. The Anglo-Saxon people brought their pagan language and culture with them. Gradually, they eliminated Christianity from their new land, except from the southeast where many Britons had fled. To address this paganization, Pope Saint Gregory the Great sent Saint Augustine of Canterbury to evangelize the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms. Over the next century, all of the Anglo-Saxon kings converted and their subjects followed. It is into this historical context that today’s saint, Saint Bede, a holy monk, profound Scripture scholar, and brilliant historian, was born and ministered.
Bede was born near a Benedictine Monastery in Wearmouth and Jarrow, modern-day Tyne and Wear, in the northeastern part of the United Kingdom. As was common at that time, Bede was given to the care of the monks of Wearmouth at the age of seven with the expectation that he would remain with them and become a monk himself. A few years later, young Bede was sent across the river to the monks’ newly founded sister monastery at Jarrow. In 686, when Bede was about thirteen years old, a severe plague ravaged the monastery, leaving only Bede and Abbot Ceolfrid alive. One of the central duties of the monks was the chanting of the Divine Office, which the oblate Bede and the abbot continued faithfully.
Of his time in the monastery, Bede himself says, “I wholly applied myself to the study of Scripture; and amidst the observance of monastic rule, and the daily charge of singing in the church, I always took delight in learning, or teaching, or writing.” After more than a decade of study and prayer under Abbot Ceolfrid, Bede was ordained to the diaconate at the age of nineteen. Eleven years later, he was ordained to the priesthood at the age of thirty. Bede describes the thirty-two years of his priestly ministry as a monk this way: “From the time when I received priest’s orders, till the fifty-ninth year of my age, I have made it my business, for my own needs and those of my brethren, to compile out of the works of the venerable Fathers, the following brief notes on the Holy Scriptures, and also to make some additions after the manner of the meaning and interpretation given by them…”
Bede was a good Benedictine monk. According to the Benedictine Rule, Bede took a vow of stability, meaning he might never have left his monastery, except possibly for occasional short visits to nearby monasteries to assist with teaching. Within his monastic cell, Bede wrote more than forty books, twenty-five of them being commentaries on the Sacred Scriptures. He also wrote books on history, rhetoric, grammar, the calculation of time, biographies, theology, and poetry.
Bede’s most famous book was written when he was fifty-nine, The Ecclesiastical History of the English People. This book begins with a description of Britain and Ireland and their ancient inhabitants. From there, he traces the role of the Roman Empire in Britain, starting with Julius Caesar until Saint Alban, the first British martyr, and on through the early Christianization of the isle. After Britain was conquered by the Anglo-Saxons in the early fifth century, Bede describes the new evangelization initiated by Pope Saint Gregory the Great at the end of the sixth century and carried out by Saint Augustine of Canterbury. The bulk of his Ecclesiastical History then focuses upon the growth of the Church in England in the sixth and seventh centuries. Most importantly, this work ties the Anglo-Saxon people back to the Church in Rome. Though the Roman Empire no longer ruled Britain, the Catholic Church centered in Rome was the country’s true spiritual ruler. Bede especially saw Pope Saint Gregory the Great as the instrument of salvation for the Anglo-Saxons to whom he belonged.
Another of Bede’s great contributions to the Universal Church was his treatise “On the Reckoning of Time,” in which he taught the correct calculation of months and years. This work was significant because it enabled the Church in England to accept the correct day on which to celebrate Easter each year. This work also helped the world establish the current calendar that begins at the birth of Christ, solidifying the use of the term Anno Domini (A.D.), “in the year of our Lord.”
Bede’s commentaries on Scripture are deeply rooted in the writings of the Church Fathers but also broke new ground. Bede follows an allegorical and a moral approach by which he interprets the various passages of Scripture in the light of the death and Resurrection of Christ, emphasizing the Scripture’s deeper symbolic meaning, rather than just giving a literal interpretation.
After his death, Bede’s works became the foundation for much learning throughout Europe. He was described by his contemporaries as “the school-master of his age” and “the candle of the Church, lit by the Holy Spirit.” His works were copied over and over again, formed monks throughout Europe, and had an undeniable influence upon the whole history of the Church. By the ninth century, Bede was referred to as the “Venerable Bede’” in two Church councils. Saint Bede’s enduring influence has been felt so strongly that more than a millennia after his death, he was declared a Doctor of the Church by Pope Leo XIII in 1899, the only Englishman to receive such an honor.
During his lifetime, Bede had a profound influence upon the monks he taught. He lived, prayed, studied, taught, and wrote from the confines of his monastery. From that place of solitude and prayer, God used him to influence all of Europe and the entire world. God can do great things when we live our vocation well. Ponder the vocation God has given you. As you do, know that your vocation is your path to holiness. Live it well, and God will bring forth His transforming presence in you and through you in ways that you could never have imagined.
Source: https://mycatholic.life/saints/saints-of-the-liturgical-year/may-25-saint-bede-the-venerable-priest-and-doctor/
Saint Bede the Venerable, Priest and Doctor Read More »